Whiplash and How to Treat it
Whiplash & Whiplash Associated Disorder
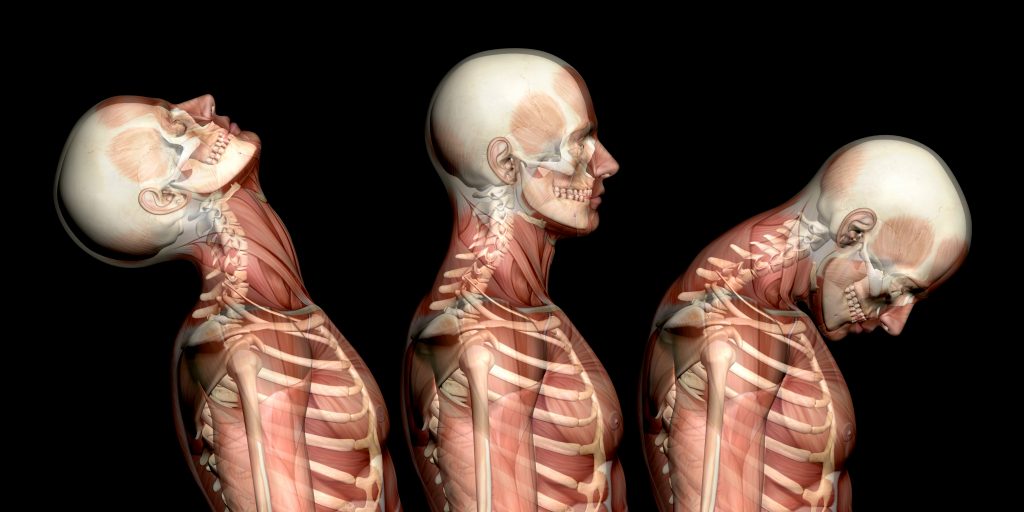
Whiplash, a very common ailment that plagues a lot of car accident victims. I am here to tell you the mechanism behind it, as well as explaining why it can very easily turn into a chronic issue and how we can look to resolve it.
Because of this, defining the difference between whiplash and whiplash-associated disorder is helpful:
- Whiplash: A description of the mechanism of injury AND a diagnosis. This includes neck (most common symptom), back, face, arm and shoulder blade pain.
- Whiplash-associated disorder (WAD): A diagnosis based on possessing such symptoms like tingling/heaviness in the arms, dizziness, ringing in ears, visual changes, poor concentration/memory and difficulty sleeping.
Because whiplash and WAD is so heavily related to car accidents, it’s appropriate to start the explanation there. For instance, whiplash affects 50-80% of car accident victims. It is a condition that is present in 300-600 North Americans and Europeans out of 100,000. In addition, there are 1,500 claims made every day which costs the industry £2 billion a year.
Firstly, whiplash occurs after a quick acceleration/deceleration, which causes damage to the bony or soft tissue of the neck. Secondly, there are 5 classifications of whiplash & WAD, listed below in the table.
Grade | Classification |
0 | No complaint in the neck or physical signs. |
I | Complaint of neck pain, stiffness or tenderness only. |
II | Neck complaint and musculoskeletal signs (reduced range of motion and tenderness). |
III | Neck complaint and neurological signs (reflexes/weakness/sensory). |
VI | Neck complaint and fracture/dislocation. |
Firstly, what should I be experiencing?
Whiplash presents with neck pain, headaches, stiffness, arm pain and paraesthesia, problems with memory/concentration and psychological distress. It is typical for pain to come on after the event.
Whiplash associated disorder is considered if whiplash patients experience other symptoms in addition to neck pain. For instance, this could be pain in other areas of the spine, paraesthesia, fatigue, nausea, cognitive problems, low self‐reported physical and mental health, depressive mood and anxiety, acute stress response and pain in multiple sites, most commonly in the posterior trunk region.
Psychosomatic element
Moreover, one of the major issues whiplash can cause is chronic widespread pain. Therefore, this is a condition that can be devastating, which is a feature of fibromyalgia.
Whiplash associated disorder is also heavily linked with early post-traumatic stress disorder and pain catastrophising. This could be due to central sensitisation, a neurological disorder that is the long term development of pain, can create of positive feedback loop for pain and stress.
For instance, pain is an interesting subject, the leading experts in the industry suggest both the experience of pain and indeed the relief of pain are complex emotional experiences, and are comprised of feelings and emotional consequences. In addition, pain is not portrayed as a blank canvas, and is completely down to interpretation in the brain, so depending on the emotional state of the person pain will feel different in quality and intensity. For instance if we take what was said at the start, about how much money is awarded to victims of a road traffic accident and consider how long you are required to be in pain for before the pay-out, it could be reasonable to assume that the reward for being in pain may transend the sensation into chronicity.
What treatment options are available?
At the Movement and Wellbeing Clinic we will evaluate the extent of the damage and ask questions about the incident (if there was one) and go through a series of tests to determine the course and extent of the damage. In addition, as neck pain can be related to neurological damage, the chances are we will conduct a full neurological screening to make sure we have tested for any potential underlying nerve damage.
For instance, treatment has shown manipulation and mobilisation therapy is more effective than exercise therapy for neck pain. Most importantly, your osteopath can mobilise the neck where the dysfunction is present which will help increase range of movement before pain starts. After that, you should start to find improvements.
Acupuncture is an effective pain reduction modality for neck pain. However, it hasn’t shown to be of benefit when reducing disability in research trials however. In other words, acupuncture with mobilisation/manipulative techniques is the preferable option.
In conclusion, exercise programs aren’t the be all and end all for treating whiplash. However once again if used alongside acupuncture and mobilisation/manipulation techniques it can become a great treatment package.
If you are suffering from the condition, please email Ed on:
info@movementandwellbeingclinic.co.uk